SWOT analysis in business and why SWOT analysis is important
Previously we were talking about the marketing strategy in an earlier post written by Anne Foster, Then we posted different posts concerning the Marketing strategy objective written by Melody Bedingfield and now we're going to talk about SWOT analysis in business and why SWOT analysis is important and swot analysis examples.
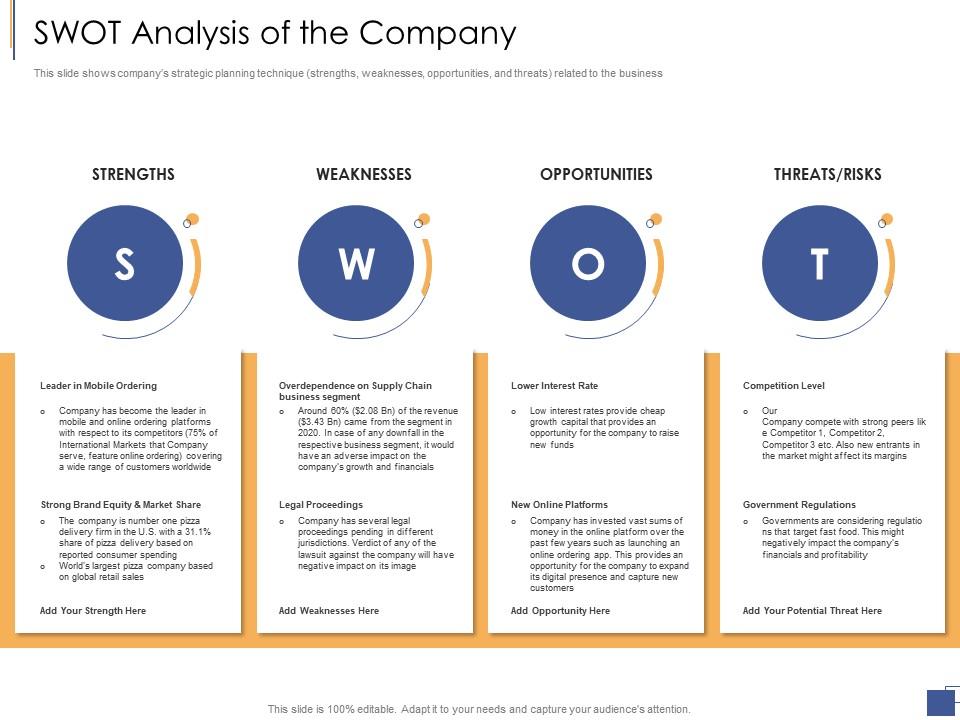
What Is SWOT Analysis?
The next thing you need to learn about is the SWOT (strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats) analysis, it’s a framework that was used to identify a company's competitive position and to enhance better strategic planning. The SWOT analysis identifies the internal and external factors, as well as current and future possibilities.
The SWOT analysis was designed to facilitate a realistic, fact-based, data-driven look at the business’s strengths and weaknesses, initiatives, or within its industry. The company needs to keep these analyses as accurate as possible by avoiding preconceived beliefs or gray areas and instead focusing on real-life contexts. The company should use it as a guide and not as important as a prescription.
How to create SWOT analysis in business?
swot analysis in business is a technique for assessing the performance, competition, risk, and potential of a business, as well as part of a business such as a product line or division, an industry, or other entity.
With the internal and external data, the technique can help businesses toward strategies more likely to succeed more, and away from those in which they have been, or are likely to be, less successful. more SWOT analysis, investors, or competitors can also guide them on whether a company, product line or industry might be strong or weak and why.
A Visual Overview
The Analysts are presenting a SWOT analysis as a square segmented into four quadrants, each dedicated to a different element of the SWOT. This visual arrangement is providing a fast quick overview of the company’s position. And these points under a particular heading may not be of similar importance, these SWOT should designate key insights into the balance of opportunities and threats, advantages and disadvantages, and so forth.
SWOT Analysis was used to analyze businesses. Now it's usually used by governments, nonprofits, and individuals, including investors and even entrepreneurs.
Strengths
Strengths are describing what a business excels at and what is separating it from the competition: a strong brand, a loyal consumer, a strong balance sheet, unique technology, etc... For example, a hedge fund may have developed a proprietary trading strategy that returns market-beating results. It must then decide how to use those results to attract new investors.
Weaknesses
Weaknesses are the things stopping a company from performing at its best level. They are fields where the business needs to improve to remain competitive: a weak brand or new brand name, above-average turnover, high levels of debt, a weak supply chain, or lack of capital.
Opportunities
Opportunities are referring to favourable external factors that can give a business some competitive advantage. For example, if some country cuts tariffs, a car manufacturer can export its cars into a new market, expanding sales and market share.
SWOT analysis threats example
SWOT analysis threats example, Threats is referring to factors that have the potential to harm a business. For example, a drought is a danger to a wheat-producing company, as it might destroy or reduce the crop yield. Other common threats include things like the increasing costs for materials, high competition, and tight labour supply.
SWOT Table
Strengths 1. What are our business competitive advantages? 2. What are the resources we have? 3. What are products that perform well? | Weaknesses 1. Where can we improve? 2. What products are not performing well? 3. Where are we lacking resources? |
Threats 1. What new regulations threaten operations? 2. What do our competitors do well? 3. What consumer trends threaten business? | Opportunities 1. What technology can we use to improve operations? 2. Can we expand our core operations? 3. What new market segments can we explore? |
What is the usage of SWOT Analysis?
Internal
What occurs within the organization is serving as a great resource of information for the strengths and weaknesses categories of our SWOT analysis.
Examples of internal factors
Including financial and human resources, tangible and intangible assets, and operational efficiencies.
These are some of the potential questions to list the internal factors:
- (Strength) What are the things we’re doing well?
- (Strength) What are our strongest assets?
- (Weakness) What are our detractors?
- (Weakness) What are the lowest-performing production lines?
External
Things happening outside of the organization is equally as important to the success of a company as the internal factors. External factors, such as monetary policies, your market changes, and access to suppliers, are some of the categories to pull from to create a list of opportunities and weaknesses.
These are some of the potential questions to list external factors:
- (Opportunity) Trends are evident in your marketplace.
- (Opportunity) The demographics our business isn’t targeting.
- (Threat) the competitor's volume and their market share.
- (Threat) New regulations that potentially can harm our operations or products?
Using SWOT analysis to identify the business challenges affecting it and opportunities that can develop it. However, note that it is one of many techniques, not a prescription.
FAQs About SWOT Analysis
What Is SWOT Analysis and Examples?
SWOT (strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats) analysis is a way of identifying and analyzing the internal strengths and weaknesses and also the external opportunities and threats that are shaping current and future operations and helping develop strategic goals. SWOT's analyses are not limited to organizations. Individuals might also use SWOT analysis to engage in constructive introspection and form improvement goals.
Home Depot is conducting a SWOT analysis, creating a balanced list of its internal benefits and disadvantages and external factors threatening the business’s market position and business growth strategy. The High-quality customer care, the strong brand name, and the positive strong relationships with suppliers were some of the notable strengths; whereas, a narrowed supply chain, interdependence on the U.S. market, and a replicable business model were listed as the weaknesses.

0 Comments
Post your comment